2.1.2.8 Tracing Options
There is more than one way to trace a ray. Sometimes there is a trade-off between quality and speed. Sometimes
options designed to make tracing faster can slow things down. This section covers options that tell POV-Ray how to
trace rays with the appropriate speed and quality settings.
Quality=n
|
Set quality value to n (0 <= n <= 11)
|
+Qn
|
Same as Quality=n
|
The Quality=n option or +Qn switch allows you to specify the image
rendering quality. You may choose to lower the quality for test rendering and raise it for final renders. The quality
adjustments are made by eliminating some of the calculations that are normally performed. For example settings below 4
do not render shadows. Settings below 8 do not use reflection or refraction. The duplicate values allow for future
expansion. The values correspond to the following quality levels:
0, 1
|
Just show quick colors. Use full ambient lighting only. Quick colors are used only at 5 or below.
|
2, 3
|
Show specified diffuse and ambient light.
|
4
|
Render shadows, but no extended lights.
|
5
|
Render shadows, including extended lights.
|
6, 7
|
Compute texture patterns, compute photons
|
8
|
Compute reflected, refracted, and transmitted rays.
|
9, 10, 11
|
Compute media and radiosity
|
The default is 9 if not specified.
2.1.2.8.2 Automatic Bounding Control
Bounding=bool
|
Turn bounding on/off
|
+MB
|
Turn bounding on; Set threshold to 25 or previous amount
|
-MB
|
Turn bounding off
|
Bounding_Threshold=n
|
Set bound threshold to n
|
+MBn
|
Turn bounding on; bound threshold to n
|
-MBn
|
Turn bounding off; set future threshold to n
|
Light_Buffer=bool
|
Turn light buffer on/off
|
+UL
|
Turn light buffer on
|
-UL
|
Turn light buffer off
|
Vista_Buffer=bool
|
Turn vista buffer on/off
|
+UV
|
Turn vista buffer on
|
-UV
|
Turn vista buffer off
|
POV-Ray uses a variety of spatial sub-division systems to speed up ray-object intersection tests. The primary
system uses a hierarchy of nested bounding boxes. This system compartmentalizes all finite objects in a scene into
invisible rectangular boxes that are arranged in a tree-like hierarchy. Before testing the objects within the bounding
boxes the tree is descended and only those objects are tested whose bounds are hit by a ray. This can greatly improve
rendering speed. However for scenes with only a few objects the overhead of using a bounding system is not worth the
effort. The Bounding=off option or -MB switch allows you to force bounding off. The default
value is on.
The Bounding_Threshold=n or +MBn switch allows you to set the minimum
number of objects necessary before bounding is used. The default is +MB25 which means that if your scene
has fewer than 25 objects POV-Ray will automatically turn bounding off because the overhead is not worth it. Generally
it is a good idea to use a much lower threshold like +MB5.
Additionally POV-Ray uses systems known as vista buffers and light buffers to further speed
things up. These systems only work when bounding is on and when there are a sufficient number of objects to meet the
bounding threshold. The vista buffer is created by projecting the bounding box hierarchy onto the screen and
determining the rectangular areas that are covered by each of the elements in the hierarchy. Only those objects whose
rectangles enclose a given pixel are tested by the primary viewing ray. The vista buffer can only be used with
perspective and orthographic cameras because they rely on a fixed viewpoint and a reasonable projection (i. e.
straight lines have to stay straight lines after the projection).
The light buffer is created by enclosing each light source in an imaginary box and projecting the bounding box
hierarchy onto each of its six sides. Since this relies on a fixed light source, light buffers will not be used for
area lights.
Reflected and transmitted rays do not take advantage of the light and vista buffer.
The default settings are Vista_Buffer=on or +UV and Light_Buffer=on or +UL.
The option to turn these features off is available to demonstrate their usefulness and as protection against
unforeseen bugs which might exist in any of these bounding systems.
In general, any finite object and many types of CSG of finite objects will properly respond to this bounding
system. In addition blobs and meshes use an additional internal bounding system. These systems are not affected by the
above switch. They can be switched off using the appropriate syntax in the scene file (see "Blob"
and "Mesh" for details).
Text objects are split into individual letters that are bounded using the bounding box hierarchy. Some CSG
combinations of finite and infinite objects are also automatically bound. The end result is that you will rarely need
to add manual bounding objects as was necessary in earlier versions of POV-Ray unless you use many infinite objects.
2.1.2.8.3 Removing User Bounding
Remove_Bounds=bool
|
Turn unnecessary bounds removal on/off
|
+UR
|
Turn unnecessary bounds removal on
|
-UR
|
Turn unnecessary bounds removal off
|
Split_Unions=bool
|
Turn split bounded unions on/off
|
+SU
|
Turn split bounded unions on
|
-SU
|
Turn split bounded unions off
|
Early versions of POV-Ray had no system of automatic bounding or spatial sub-division to speed up ray-object
intersection tests. Users had to manually create bounding boxes to speed up the rendering. Since version 3.0, POV-Ray
has had more sophisticated automatic bounding than any previous version. In many cases the manual bounding on older
scenes is slower than the new automatic systems. Therefore POV-Ray removes manual bounding when it knows it will help.
In rare instances you may want to keep manual bounding. Some older scenes incorrectly used bounding when they should
have used clipping. If POV-Ray removes the bounds in these scenes the image will not look right. To turn off the
automatic removal of manual bounds you should specify Remove_Bounds=off or use -UR. The
default is Remove_Bounds=on.
One area where the jury is still out is the splitting of manually bounded unions. Unbounded unions are always split
into their component parts so that automatic bounding works better. Most users do not bound unions because they know
that doing so is usually slower. If you do manually bound a union we presume you really want it bound. For safety sake
we do not presume to remove such bounds. If you want to remove manual bounds from unions you should specify Split_Unions=on
or use +SU. The default is Split_Unions=off.
2.1.2.8.4 Anti-Aliasing Options
Antialias=bool
|
Turns anti-aliasing on/off
|
+A
|
Turns aa on with threshold 0.3 or previous amount
|
-A
|
Turns anti-aliasing off
|
Sampling_Method=n
|
Sets aa-sampling method (only 1 or 2 are valid)
|
+AMn
|
Same as Sampling_Method=n
|
Antialias_Threshold=n.n
|
Sets anti-aliasing threshold
|
+An.n
|
Sets aa on with aa-threshold at n.n
|
-An.n
|
Sets aa off (aa-threshold n.n in future)
|
Jitter=bool
|
Sets aa-jitter on/off
|
+J
|
Sets aa-jitter on with 1.0 or previous amount
|
-J
|
Sets aa-jitter off
|
Jitter_Amount=n.n
|
Sets aa-jitter amount to n.n. If n.n <= 0 aa-jitter is set off
|
+Jn.n
|
Sets aa-jitter on; jitter amount to n.n. If n.n <= 0 aa-jitter is set off
|
-Jn.n
|
Sets aa-jitter off (jitter amount n.n in future)
|
Antialias_Depth=n
|
Sets aa-depth (1 <= n <= 9)
|
+Rn
|
Same as Antialias_Depth=n
|
The ray-tracing process is in effect a discrete, digital sampling of the image with typically one sample per pixel.
Such sampling can introduce a variety of errors. This includes a jagged, stair-step appearance in sloping or curved
lines, a broken look for thin lines, moiré patterns of interference and lost detail or missing objects, which
are so small they reside between adjacent pixels. The effect that is responsible for those errors is called aliasing.
Anti-aliasing is any technique used to help eliminate such errors or to reduce the negative impact they have on the
image. In general, anti-aliasing makes the ray-traced image look smoother. The Antialias=on
option or +A switch turns on POV-Ray's anti-aliasing system.
When anti-aliasing is turned on, POV-Ray attempts to reduce the errors by shooting more than one viewing ray into
each pixel and averaging the results to determine the pixel's apparent color. This technique is called super-sampling
and can improve the appearance of the final image but it drastically increases the time required to render a scene
since many more calculations have to be done.
POV-Ray gives you the option to use one of two alternate super-sampling methods. The Sampling_Method=n
option or +AMn switch selects either type 1 or type 2. Selecting one
of those methods does not turn anti-aliasing on. This has to be done by using the +A command line switch
or Antialias=on option.
Type 1 is an adaptive, non-recursive, super-sampling method. It is adaptive because not every pixel is
super-sampled. Type 2 is an adaptive and recursive super-sampling method. It is recursive because the pixel
is sub-divided and sub-sub-divided recursively. The adaptive nature of type 2 is the variable depth of
recursion.
In the default, non-recursive method (+AM1), POV-Ray initially traces one ray per pixel. If the color
of a pixel differs from its neighbors (to the left or above) by at least the set threshold value then the pixel is
super-sampled by shooting a given, fixed number of additional rays. The default threshold is 0.3 but it may be changed
using the Antialias_Threshold=n.n option. When the switches are used, the threshold may
optionally follow the +A. For example +A0.1 turns anti-aliasing on and sets the threshold
to 0.1.
The threshold comparison is computed as follows. If r1, g1, b1 and r2, g2, b2 are the rgb components of two pixels
then the difference between pixels is computed by
diff = abs(r1-r2) + abs(g1-g2) + abs(b1-b2)
If this difference is greater than the threshold then both pixels are super-sampled. The rgb values are in the
range from 0.0 to 1.0 thus the most two pixels can differ is 3.0. If the anti-aliasing threshold is 0.0 then every
pixel is super-sampled. If the threshold is 3.0 then no anti-aliasing is done. Lower threshold means more
anti-aliasing and less speed. Use anti-aliasing for your final version of a picture, not the rough draft. The lower
the contrast, the lower the threshold should be. Higher contrast pictures can get away with higher tolerance values.
Good values seem to be around 0.2 to 0.4.
When using the non-recursive method, the default number of super-samples is nine per pixel, located on a 3*3 grid.
The Antialias_Depth=n option or +Rn switch controls the number of rows
and columns of samples taken for a super-sampled pixel. For example +R4 would give 4*4=16 samples per
pixel.
The second, adaptive, recursive super-sampling method starts by tracing four rays at the corners of each pixel. If
the resulting colors differ more than the threshold amount additional samples will be taken. This is done recursively,
i.e. the pixel is divided into four sub-pixels that are separately traced and tested for further subdivision. The
advantage of this method is the reduced number of rays that have to be traced. Samples that are common among adjacent
pixels and sub-pixels are stored and reused to avoid re-tracing of rays. The recursive character of this method makes
the super-sampling concentrate on those parts of the pixel that are more likely to need super-sampling (see figure
below).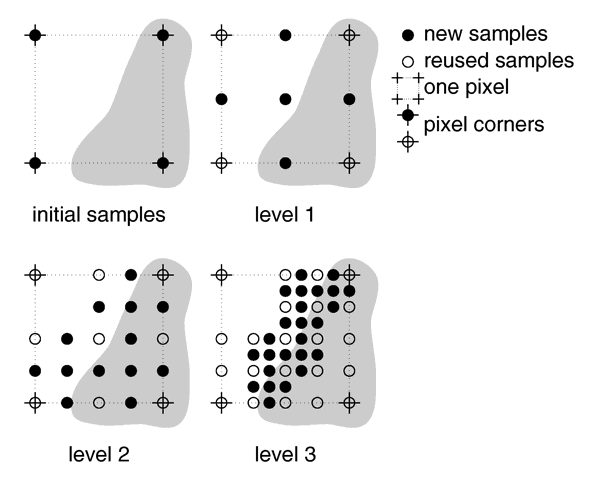
The maximum number of subdivisions is specified by the Antialias_Depth=n option or +Rn
switch. This is different from the adaptive, non-recursive method where the total number of super-samples is
specified. A maximum number of n subdivisions results in a maximum number of samples per pixel that is given
by the following table.
+Rn
|
Number of additional samples per super-sampled pixel for the non-recursive method +AM1
|
Maximum number of samples per super-sampled pixel for the recursive method +AM2
|
1
|
1
|
9
|
2
|
4
|
25
|
3
|
9
|
81
|
4
|
16
|
289
|
5
|
25
|
1089
|
6
|
36
|
4225
|
7
|
49
|
16641
|
8
|
64
|
66049
|
9
|
81
|
263169
|
Note: the maximum number of samples in the recursive case is hardly ever reached for
a given pixel. If the recursive method is used with no anti-aliasing each pixel will be the average of the rays traced
at its corners. In most cases a recursion level of three is sufficient.
Another way to reduce aliasing artefacts is to introduce noise into the sampling process. This is called jittering
and works because the human visual system is much more forgiving to noise than it is to regular patterns. The location
of the super-samples is jittered or wiggled a tiny amount when anti-aliasing is used. Jittering is used by default but
it may be turned off with the Jitter=off option or -J switch. The amount of jittering can be
set with the Jitter_Amount=n.n option. When using switches the jitter scale may be specified
after the +Jn.n switch. For example +J0.5 uses half the normal jitter. The default
amount of 1.0 is the maximum jitter which will insure that all super-samples remain inside the original pixel.
Note: the jittering noise is random and non-repeatable so you should avoid using
jitter in animation sequences as the anti-aliased pixels will vary and flicker annoyingly from frame to frame.
If anti-aliasing is not used one sample per pixel is taken regardless of the super-sampling method specified.
More about "Mesh"
|






